Waves
A wave is a kind of oscillation (disturbance) that
travels through space and matter. Wave motions transfer energy from one place
to another.
Types of waves
1.Transverse waves
Transverse waves are wave in which the vibrations of the particles or
medium in which the wave travels are at right angles to the direction in which
the wave travels.
Example : Water waves
2.Longitudinal waves
Longitudinal waves are wave in which the vibrations of the particles or
medium in which the wave travels are in the same direction as to that in which
the wave travels.
Example : Sound waves
Frequency
Frequency describes the number of waves that pass a fixed
place in a given amount of time. So if the time it takes for a wave to pass is
is 1/2 second, the frequency is 2 per second. If it takes 1/100 of an hour, the
frequency is 100 per hour.
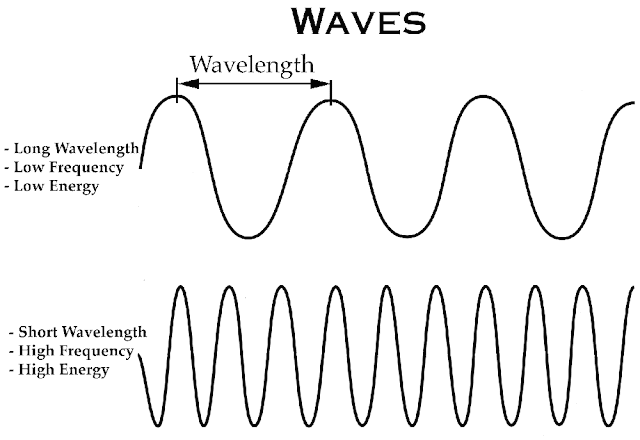
Wavelength
The wavelength and frequency of light are closely
related. The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength. Because all
light waves move through a vacuum at the same speed, the number of wave crests
passing by a given point in one second depends on the wavelength.
2G Spectrum
2G (or 2-G) is short for second-generation wireless telephone technology. It is based on narrow band digital networks.
Signals is transmitted in the digital format and this dramatically improved the quality of calls and also reduced the complexity of data transmission.
3G Spectrum
3G, short form of third generation, is the third generation of mobile telecommunications technology.This is based on a set of standards used for mobile devices and mobile telecommunications use services and networks.
3G telecommunication networks support services that provide an information transfer rate of at least 200 kbit/s.





