The PHP Hypertext
Preprocessor (PHP) is a programming language that allows web developers to
create dynamic content that interacts with databases.
- PHP is a server scripting language, and a powerful tool for making dynamic and interactive Web pages.
- PHP is a widely-used, free, and efficient alternative to competitors such as Microsoft's ASP.
- PHP is an acronym for "PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor"
- PHP is a widely-used, open source scripting language
- PHP scripts are executed on the server
- PHP is free to download and use
Before you continue
you should have a basic understanding of the following:
- HTML
- CSS
- JavaScript
PHP Syntax
A PHP script is
executed on the server, and the plain HTML result is sent back to the browser.
Basic PHP Syntax
A PHP script can be
placed anywhere in the document.
A PHP script starts
with <?php and ends with ?>:
<?php
// PHP code goes here
?>
The default file
extension for PHP files is ".php".
A PHP file normally
contains HTML tags, and some PHP scripting code.
Example
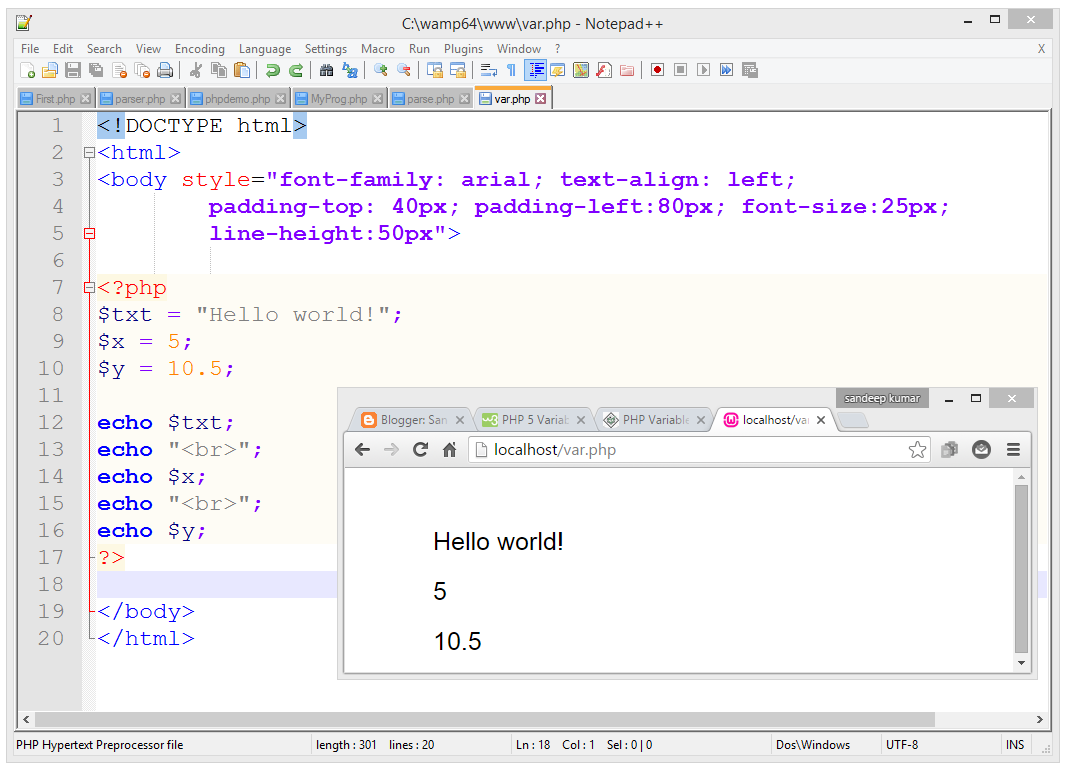
PHP Variables
The main way to store
information in the middle of a PHP program is by using a variable.
PHP has a total of eight data types which we use to construct our
variables −
- Integers − are whole numbers, without a decimal point, like 4195.
- Doubles − are floating-point numbers, like 3.14159 or 49.1.
- Booleans − have only two possible values either true or false.
- NULL − is a special type that only has one value: NULL.
- Strings − are sequences of characters, like 'PHP supports string operations.'
- Arrays − are named and indexed collections of other values.
- Objects − are instances of programmer-defined classes, which can package up both other kinds of values and functions that are specific to the class.
- Resources − are special variables that hold references to resources external to PHP (such as database connections).
Example
PHP echo and
print Statements
In PHP there are two
basic ways to get output: echo and print.
echo and print are
more or less the same. They are both used to output data to the screen.
The differences are
small: echo has no return value while print has a return value of 1 so it can
be used in expressions. echo can take multiple parameters (although such usage
is rare) while print can take one argument. echo is marginally faster than print.
The PHP echo Statement
The echo statement can
be used with or without parentheses: echo or echo().
Display Text
The following example
shows how to output text with the echo command (notice that the text can
contain HTML markup):
Example
The PHP print Statement
The print statement
can be used with or without parentheses: print or print().
Display Text
The following example
shows how to output text with the print command (notice that the text can
contain HTML markup):
Example
PHP Data Types
Variables can store
data of different types, and different data types can do different things.
PHP supports the
following data types:
- String
- Integer
- Float (floating point numbers - also called double)
- Boolean
- Array
- Object
- NULL
- Resource
PHP Conditional Statements
Very often when you
write code, you want to perform different actions for different conditions. You
can use conditional statements in your code to do this.
In PHP we have the
following conditional statements:
- if statement - executes some code if one condition is true
- if...else statement - executes some code if a condition is true and another code if that condition is false
- if...elseif....else statement - executes different codes for more than two conditions
- switch statement - selects one of many blocks of code to be executed
PHP - The if Statement
The if statement
executes some code if one condition is true.
Syntax
if (condition)
{
code to be
executed if condition is true;
}
Example
PHP - The if...else
Statement
The if....else
statement executes some code if a condition is true and another code if that
condition is false.
Syntax
if (condition)
{
code to be
executed if condition is true;
}
else
{
code to be
executed if condition is false;
}
Example
PHP - The
if...elseif....else Statement
The
if....elseif...else statement executes different codes for more than two
conditions.
Syntax
if (condition)
{
code to be
executed if this condition is true;
}
elseif (condition)
{
code to be
executed if this condition is true;
}
else
{
code to be
executed if all conditions are false;
}
Example
The PHP switch
Statement
Use the switch
statement to select one of many blocks of code to be executed.
Syntax
switch (n)
{
case
label1:
code
to be executed if n=label1;
break;
case
label2:
code
to be executed if n=label2;
break;
case
label3:
code
to be executed if n=label3;
break;
...
default:
code
to be executed if n is different from all labels;
}
Example
PHP - Loop Types
Loops in PHP are used
to execute the same block of code a specified number of times. PHP supports
following four loop types.
for −
loops through a block of code a specified number of times.
while −
loops through a block of code if and as long as a specified condition is true.
do...while −
loops through a block of code once, and then repeats the loop as long as a
special condition is true.
foreach −
loops through a block of code for each element in an array.
The PHP for Loop
The for loop is used
when you know in advance how many times the script should run.
Syntax
for (init counter; test counter; increment counter)
{
code to be
executed;
}
The PHP while Loop
The while loop
executes a block of code as long as the specified condition is true.
Syntax
while (condition is true)
{
code to be
executed;
}
The PHP do...while Loop
The do...while loop
will always execute the block of code once, it will then check the condition,
and repeat the loop while the specified condition is true.
Syntax
do
{
code to be
executed;
}
The PHP foreach Loop
The foreach loop works
only on arrays, and is used to loop through each key/value pair in an array.
Syntax
foreach ($array as $value)
{
code to be
executed;
}
Example

PHP User Defined
Functions
Besides the built-in
PHP functions, we can create our own functions.
A function is a block
of statements that can be used repeatedly in a program.
A function will not
execute immediately when a page loads.
A function will be
executed by a call to the function.
Create a User Defined
Function in PHP
A user defined
function declaration starts with the word "function":
Syntax
function
functionName()
{
code to be executed;
}
PHP Arrays
An array stores
multiple values in one single variable:
An array is a special
variable, which can hold more than one value at a time.
If you have a list of
items (a list of car names, for example), storing the cars in single variables
could look like this:
$cars1 =
"Volvo";
$cars2 =
"BMW";
$cars3 =
"Toyota";
In PHP, the array()
function is used to create an array:
array();
In PHP, there are
three types of arrays:
Indexed arrays -
Arrays with a numeric index
Associative arrays -
Arrays with named keys
Multidimensional
arrays - Arrays containing one or more arrays
PHP 5 File Handling
File handling is an
important part of any web application. You often need to open and process a
file for different tasks.
PHP Manipulating Files
PHP has several
functions for creating, reading, uploading, and editing files.
PHP readfile()
Function
The readfile()
function reads a file and writes it to the output buffer.
Assume we have a text
file called "webdictionary.txt", stored on the server, that looks
like this:
Example
<?php
echo
readfile("webdictionary.txt");
?>
PHP Open File -
fopen()
A better method to
open files is with the fopen() function. This function gives you more options
than the readfile() function.
We will use the text
file, "webdictionary.txt", during the lessons:
<?php
$myfile =
fopen("webdictionary.txt", "r") or die("Unable to open
file!");
echo
fread($myfile,filesize("webdictionary.txt"));
fclose($myfile);
?>
PHP Read File -
fread()
The fread() function
reads from an open file.
The first parameter of
fread() contains the name of the file to read from and the second parameter
specifies the maximum number of bytes to read.
The following PHP code
reads the "webdictionary.txt" file to the end:
fread($myfile,filesize("webdictionary.txt"));
PHP Close File -
fclose()
The fclose() function
is used to close an open file.
The fclose() requires
the name of the file (or a variable that holds the filename) we want to close:
<?php
$myfile =
fopen("webdictionary.txt", "r");
// some code to be
executed....
fclose($myfile);
?>
PHP Read Single Line -
fgets()
The fgets() function
is used to read a single line from a file.
The example below
outputs the first line of the "webdictionary.txt" file:
Example
<?php
$myfile =
fopen("webdictionary.txt", "r") or die("Unable to open
file!");
echo fgets($myfile);
fclose($myfile);
?>
PHP Read Single
Character - fgetc()
The fgetc() function
is used to read a single character from a file.
The example below
reads the "webdictionary.txt" file character by character, until
end-of-file is reached:
Example
<?php
$myfile =
fopen("webdictionary.txt", "r") or die("Unable to open
file!");
// Output one
character until end-of-file
while(!feof($myfile))
{
echo fgetc($myfile);
}
fclose($myfile);
?>