Microsoft Excel is a
spreadsheet program that is used to store, sort and efficiently crunch numbers.
Accountants use Excel to keep track of transactions for their company.
Create a new workbook
Excel documents are
called workbooks.Each workbook has sheets, typically called spreadsheets. You
can add as many sheets as you want to a workbook, or you can create new
workbooks to keep your data separate.
Click File > New.
Under New, click the
Blank workbook.
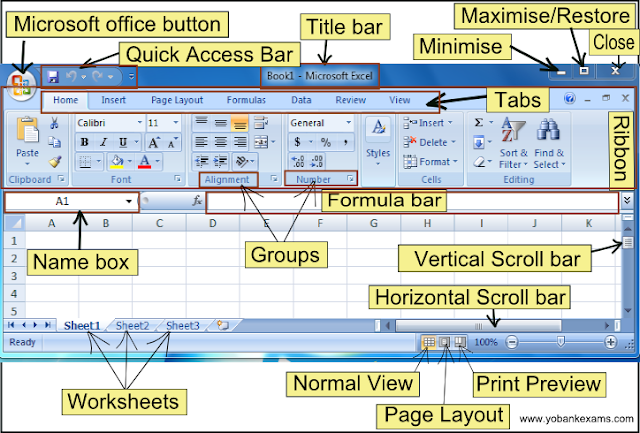

- Microsoft office button:This is a round button that you can see on the uppermost left corner of the workbook.You can use this to open a new workbook or save.We will be exploring the options under this head in detail in the next lesson.
- Quick Acess Toolbar:There is a small bar right next to the Microsoft Office button.You can customise and add frequently used commands to the quick access tool bar so that you access any command at a click.
- Title bar:Title bar appears at the top of any worksheet.
- By default the 1st sheet you open is named as Book1 which you can rename by saving it with a different name.
- Minimise:There is minus(-)like symbol to the topmost right corner of the worksheet which you can use to minimise the window
- Maximise/Restore down:Next to the minimise button is a box shaped button which you can use to maximise or restore the window.
- Close:Next to Maximise button is Cross(x)sign which you can use to close the window.
- Ribbon:The whole area to the bottom of the title bar is the Ribbon.
- Tabs:Ribbon is divided into different tabs based on the functions they perform.We have the Home tab,Insert tab,Pagelayout tab,Formulas tab,Data tab, Review tab, View tab.
- Groups;All similar type of commands are grouped together into a group.
- Ex:Alignment and Number are groups.
- Name box:To the left corner below the Ribbon is the name box which shows the active cell/cell reference.
- Formula bar:The white area next to fx is the formula bar which you can use to insert formulas.
- Vertical scroll bar:To right of the worksheet is the vertical scroll bar which you can use to scroll to see more data on the vertical side.
- Horizontal scroll bar:To the bottom right of the worksheet is the horizontalscroll bar which you can use to scroll to see more data on the horizontal side.
- Normal View:Below the horizontal scroll bar there is an icon called normal view which you can use to view the worksheet in the normal mode.
- Page Layout:Below the horizontal scroll bar there is another icon in the middle called Page Layout which allows you to modify the page layout.
- Print Preview:Below the horizontal scroll bar next to Page layout is the Print Preview button which shows you how the worksheet looks when you print it.
Enter your data
Click an empty cell.
For example, cell A1 on a new sheet.
Cells are referenced
by their location in the row and column on the sheet, so cell A1 is in the
first row of column A.
Type text or a number
in the cell.
Press Enter or Tab to
move to the next cell.
Use AutoSum to add your data
When you’ve entered
numbers in your sheet, you might want to add them up. A fast way to do that is
by using AutoSum.
Select the cell to the
right or below the numbers you want to add.
Click Home >
AutoSum, or press Alt+=.
AutoSum adds up the
numbers and shows the result in the cell you selected.
Create a simple formula
Adding numbers is just
one of the things you can do, but Excel can do other math too. Try some simple
formulas to add, subtract, multiply or divide your numbers.
Pick a cell and type
an equal sign (=). That tells Excel that this cell will contain a formula.
Type a combination of
numbers and calculation operators, like the plus sign (+) for addition, the
minus sign (-) for subtraction, the asterisk (*) for multiplication, or the
forward slash (/) for division.
For example, enter
=2+4, =4-2, =2*4, or =4/2.
Press Enter. That runs
the calculation.
You can also press
Ctrl+Enter if you want the cursor to stay on the active cell.
Apply a number format
To distinguish between
different types of numbers, add a format, like currency, percentages, or dates.
Select the cells that
have numbers you want to format.
Put your data in a table
A simple way to access
a lot of Excel’s power is to put your data in a table. That lets you quickly
filter or sort your data for starters.
Select your data by
clicking the first cell and dragging to the last cell in your data.
To use the keyboard,
hold down Shift while you press the arrow keys to select your data.
Click the Quick
Analysis button in
the bottom-right corner of the selection.
Click Tables, move
your cursor to the Table button so you can see how your data will look. If you
like what you see, click the button.
Now you can play with
your data: Filter to see only the data you want, or sort it to go from, say,
largest to smallest. Click the arrow Filter drop-down arrow in the table header
of a column.
To filter data,
uncheck the Select All box to clear all check marks, and then check the boxes
of the data you want to show in your table.
Click Print.
Show totals for your numbers
Quick Analysis tools
let you total your numbers quickly. Whether it’s a sum, average, or count you
want, Excel shows the calculation results right below or next to your numbers.
Select the cells that
contain numbers you want to add or count.
Click the Quick
Analysis button Quick Analysis button in
the bottom-right corner of the selection.
Click Totals, move
your cursor across the buttons to see the calculation results for your data,
and then click the button to apply the totals.
Add meaning to your data
Select the data you
want to examine more closely.
Click the Quick
Analysis button that appears in the
lower-right corner of your selection.
For example, pick a
color scale in the Formatting gallery to differentiate high, medium, and low
temperatures.
When you like what you
see, click that option.
Show your data in a chart
The Quick Analysis
tool recommends the right chart for your data and gives you a visual
presentation in just a few clicks.
Select the cells that
contain the data you want to show in a chart.
Click the Quick
Analysis button that appears in the
lower-right corner of your selection.
Click Charts, move
across the recommended charts to see which one looks best for your data, and
then click the one that you want.
Save your work
Click the Save button
on the Quick Access Toolbar, or press Ctrl+S.
Save button on the
Quick Access Toolbar
If you’ve saved your
work before, you’re done.
If this is the first
time, go on to complete the next steps:
Under Save As, pick
where to save your workbook, and then browse to a folder.
In the File name box,
enter a name for your workbook.
Click Save to finish.
Print
Click File > Print,
or press Ctrl+P.
Preview the pages by
clicking the Next Page and Previous Page arrows.
The preview window
displays the pages in black and white or in color, depending on your printer
settings.
If you don’t like how
your pages will be printed, you can change page margins or add page breaks.